The inception of a fashion brand in the early 1990s sparked a revolution in style and sustainability. Initially, the brand focused on simple designs and basic materials, but it has since evolved to embrace cutting-edge fashion technology and eco-friendly practices. Today, the brand is known for its innovative use of sustainable fabrics and ethical production methods, which have garnered a loyal following. Key advancements in design, such as the incorporation of recycled materials and limited-edition collections, have continuously enhanced its appeal while minimizing environmental impact. As you delve into the brand's journey, you'll discover how it has transformed the fashion industry and how ongoing innovations are paving the way for a more sustainable future in fashion.
Rudolf Diesel's Early Life

In the mid-19th century, Rudolf Diesel's early life in Paris laid the groundwork for his future innovations in engineering. Born in 1858, he exhibited an early fascination with thermodynamics, which would later influence his work on engines. As a refrigeration engineer, you'd find that Diesel gained a decade of hands-on experience with various heat engines, allowing him to understand the intricacies of energy conversion.
His initial experiments included a solar-powered air engine, showcasing his innovative spirit and desire to harness alternative energy sources. However, it was his shift towards combustion engines that marked a pivotal moment in his career. By collaborating with Maschinenfabrik-Augsburg AG, Diesel refined his ideas, leading to significant advancements in engine technology. His relentless pursuit of efficiency and power in engines culminated in 1892 when he secured patents for his groundbreaking designs.
Ultimately, Diesel's efforts paid off. By 1898, he became a millionaire, a proof of the commercial success and widespread adoption of his diesel engine technology. This trajectory not only highlights Diesel's engineering prowess but also underscores the transformative impact of his early experiences on his later achievements.
Invention of the Diesel Engine
Rudolf Diesel's invention of the diesel engine marked a revolutionary shift in the landscape of power generation and transportation. In 1892, Diesel patented his design for the first compression ignition engine, aiming for unprecedented efficiency. By 1897, he successfully demonstrated the first diesel engine prototype, achieving an impressive efficiency of 26.2%. This was a significant leap compared to the steam engines of the time, which often struggled with energy losses.
The one-cylinder, four-stroke configuration of Diesel's engine utilized heat from compressed air to ignite the fuel, enhancing its overall performance. His vision for the diesel engine was to empower independent craftsmen and provide a reliable alternative to the dominant steam engines, which were often cumbersome and inefficient.
As the history of diesel unfolded, the versatility of Diesel's invention became evident. Diesel engines quickly found applications in submarines, ships, locomotives, and trucks, fundamentally transforming transportation and industrial processes. This remarkable achievement not only paved the way for future innovations but also established the diesel engine as a cornerstone of modern engineering and industrial efficiency.
Diesel Engine Efficiency Improvements

Over the years, diesel engine efficiency has seen remarkable improvements, evolving from Rudolf Diesel's original prototype efficiency of 26.2% in 1897 to modern engines that exceed 40%. This significant leap showcases advancements in diesel technology, pushing the boundaries of engine efficiency. Turbocharging, introduced by Alfred Büchi in 1925, revolutionized these engines by enhancing air intake and combustion, allowing you to harness more power from less fuel.
Furthermore, the advent of direct fuel injection systems has transformed how fuel is delivered into the combustion chamber. These systems create improved fuel spray patterns, resulting in more efficient combustion and lower emissions. You'll find that continuous innovations, particularly from companies like Cummins in the mid-2000s, have focused on enhancing fuel economy while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
These advancements not only improve fuel efficiency but also contribute to better overall performance, making modern diesel engines a more environmentally friendly choice. As you explore the evolution of diesel engines, it's clear that each technological breakthrough has played a critical role in refining engine efficiency and meeting the demands of today's world.
Applications of Diesel Engines
Diesel engines play an essential role in various sectors, showcasing their versatility and efficiency across multiple applications. In commercial trucking, for instance, diesel engines provide higher fuel efficiency and torque compared to gasoline engines, making them the preferred choice for long-haul transport. This capability not only reduces operational costs but also enhances the sustainability of freight logistics.
In the rail industry, diesel engines have largely replaced steam engines, offering superior efficiency while effectively handling heavy loads over long distances. This change has revolutionized rail transport, allowing for greater reliability in passenger and freight services.
Marine applications also heavily rely on diesel engines, powering ships and submarines where reliability and fuel efficiency are paramount. Their ability to deliver consistent power under demanding conditions makes them vital for naval and commercial operations.
Moreover, diesel engines serve as the backbone for stand-alone generators, providing electricity in remote locations and during emergencies. They guarantee a dependable power supply when it's needed most.
In industrial settings, diesel engines drive factory equipment and construction machinery, greatly boosting productivity and operational efficiency. Overall, their diverse applications underscore the integral role diesel engines play in modern society.
Advancements in Diesel Technology
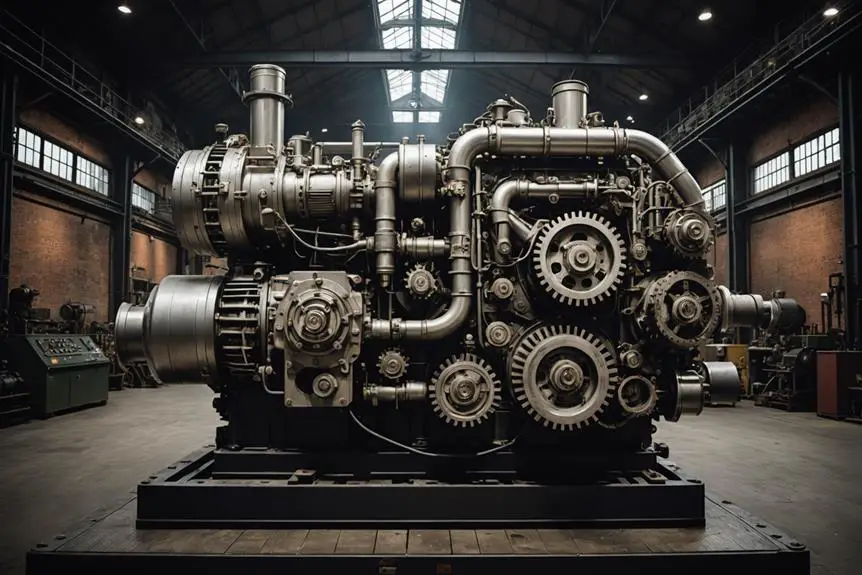
The evolution of diesel technology has markedly impacted its applications, enhancing performance and efficiency across various sectors. One key advancement was turbocharging technology, introduced by Alfred Büchi in 1925, which forced more air into the combustion chamber, boosting engine efficiency. Following this, Robert Bosch's improvements to fuel-injection pumps in 1927 allowed for more precise fuel delivery, greatly elevating overall engine performance.
In the early 2000s, the development of ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) aimed to reduce harmful emissions, marking a pivotal moment in fuel formulation. However, this new fuel required modern lubricity additives to maintain engine integrity. More recently, Cummins released next-generation diesel engines in 2017, featuring redesigned emission controls that complied with stringent regulations while still delivering robust performance.
Furthermore, innovations like flow improvers and wax anti-settling additives (WASA) have been essential for enhancing diesel fuel performance, particularly in cold weather conditions. These advancements collectively demonstrate a commitment to improving efficiency and reducing emissions, ensuring that diesel technology remains relevant and effective in an ever-evolving landscape.
Environmental Regulations Impact
Environmental regulations have profoundly shaped the landscape of diesel technology, compelling manufacturers to innovate in response to stricter emissions standards. The introduction of the Clean Air Act in 1970 set the stage for significant changes in diesel engines. Here's how these regulations have impacted the industry:
- The mid-2000s saw the rollout of ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD), drastically reducing sulfur content in diesel fuel.
- The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) established stringent particulate matter and nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions standards.
- Innovations in emissions control technologies, like selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and diesel particulate filters (DPF), became necessary.
- Adoption of Tier 4 standards in 2014 required non-road diesel engines to meet even stricter emissions criteria.
- Manufacturers faced increased pressure to design more environmentally friendly engines.
These regulations have driven the industry towards cleaner technology, enhancing air quality and public health. As a result, you're witnessing a shift not only in how diesel engines operate but also in the perception of diesel fuel itself. By adapting to these environmental regulations, manufacturers are ensuring that diesel technology remains viable in a more eco-conscious world.
Diesel Fuel Types and Characteristics

Among the various fuel options available, diesel fuel is primarily categorized into two main types: Diesel #1 and Diesel #2. Diesel #1 has lower viscosity, making it ideal for cold temperatures, guaranteeing reliable engine performance in frigid conditions. On the other hand, Diesel #2 is thicker and more cost-effective, often providing better fuel economy due to its higher energy content. This characteristic makes it the preferred choice for many applications.
Modern diesel fuels are produced through the refining of crude oil and biomass materials, resulting in various grades that meet specific performance and environmental standards. The introduction of ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) has greatly improved air quality but has also necessitated modern lubricity additives to counteract the loss of natural lubricity in diesel fuels.
Furthermore, biodiesel has emerged as a renewable alternative, derived from plant oils and animal fats. To guarantee compatibility and quality, biodiesel must meet ASTM D6751 standards. The choice between Diesel #1, Diesel #2, and biodiesel can greatly influence engine efficiency, making it essential to understand their characteristics for peak performance.
Diesel Engines in Transportation
Diesel engines have transformed the landscape of transportation, combining efficiency and reliability in a way that few alternatives can match. They became dominant in commercial trucking by the 1960s, proving superior in fuel efficiency and durability over gasoline engines. The versatility of diesel technology was first showcased in 1936 with the introduction of the first diesel passenger vehicle by Mercedes-Benz.
Today, modern diesel engines are used to power a variety of transportation modes, including:
- Trucks for freight and logistics
- Trains for long-distance travel and cargo
- Buses for public transit systems
- Boats for maritime transport
- Generators for emergency power supply
The diesel engines of today can achieve over 40% efficiency, far exceeding the capabilities of earlier steam engines, which typically operated at around 10% efficiency. This remarkable efficiency not only supports global logistics and transit systems but also emphasizes their essential role in diverse applications, from commercial vehicles to generators in remote areas. Understanding the history of the diesel allows you to appreciate the pivotal role these engines continue to play in shaping modern transportation.
Innovations by Cummins Engine Company
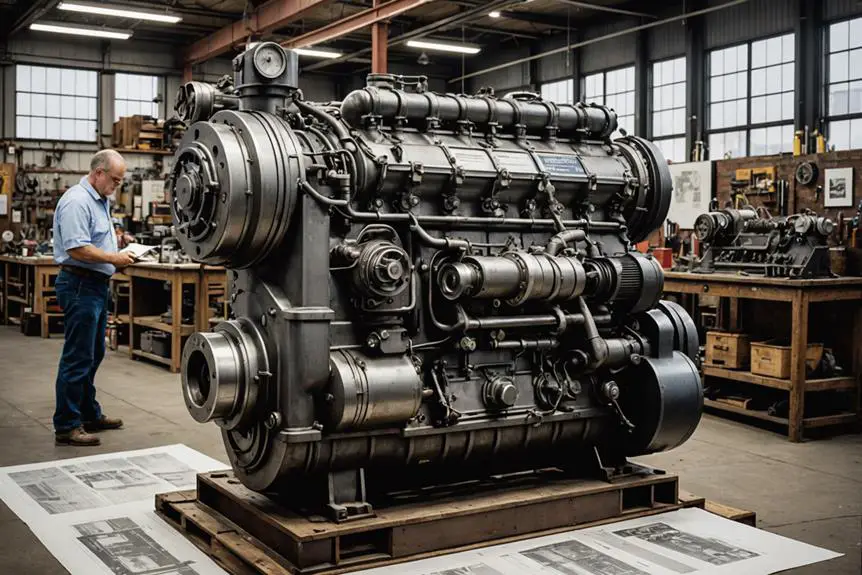

The evolution of diesel technology is closely linked to the innovations spearheaded by the Cummins Engine Company. Founded in 1919 by Clessie Cummins, this company has consistently pushed the boundaries of diesel engine performance through groundbreaking engineering and design. One of their notable achievements came in 1924 with the introduction of the Model F Engine, which featured a patented direct-injection design that greatly enhanced fuel efficiency and overall performance.
By 1928, Cummins had set a new standard in the industry with the Model U engine, showcasing remarkable advancements in power and reliability. As environmental concerns intensified, Cummins has focused on carbon neutrality and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, leading to continuous upgrades in their diesel engines. The X15 engine exemplifies this commitment, combining efficiency with high performance.
Moreover, Cummins has demonstrated its dedication to reliable diesel technology through major projects like the delivery of 400 QSK19 engines for the VLocity rail project. These innovations not only reflect Cummins' engineering prowess but also its role in shaping the future of diesel engines, emphasizing a balance between performance and sustainability.
Future of Diesel Technology
As the demand for cleaner energy solutions grows, the future of diesel technology is evolving rapidly to meet both performance and environmental standards. The industry is focusing on innovative approaches to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while maintaining engine efficiency. Here are some key trends reshaping the future of diesel:
- Development of carbon-neutral fuels
- Enhanced emissions control systems
- Increased integration of biodiesel and renewable diesel
- Innovations in waste-heat recovery systems
- Investment in turbocharging and advanced fuel injection technologies
Manufacturers are redesigning diesel engines with sophisticated emissions controls to comply with stringent regulations. The use of renewable diesel, along with biodiesel, is becoming more mainstream, markedly lowering the carbon footprint of diesel-powered vehicles. Furthermore, research into waste-heat recovery systems is essential, as it improves the overall sustainability of diesel technology.
The ongoing investment in turbocharging and fuel injection systems promises to boost performance and efficiency across various applications, from transportation to power generation. In this evolving landscape, the future of diesel technology looks bright, offering solutions that balance operational demands with environmental responsibilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Brief History of Diesel Fuel?
Diesel fuel evolved through key advancements, including the introduction of Diesel #1 and #2 for varying conditions. Later, ultra-low sulfur diesel addressed environmental concerns, while biodiesel offered a renewable alternative, enhancing fuel options for modern engines.
What Is the Story Behind Diesel?
You'll find that diesel's story revolves around Rudolf Diesel's pursuit of efficiency, leading to his patented engine design. This innovation transformed energy consumption, impacting transportation and industry, while paving the way for sustainable fuel options.
When Did Diesel Start Being Used?
Diesel engines started being used in marine applications around 1900, with their efficiency making them ideal for powering ships. By the 1930s, they entered the automotive sector, transforming transportation and commercial trucking industries considerably.
Who Invented Diesel?
You'll find that Rudolf Diesel invented the diesel engine, securing patent #608845 in 1892. His innovative design focused on improving efficiency and heat transference, revolutionizing power generation for various industries and applications worldwide.





Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?